Transit's greatest potential to attract drivers from cars is the work trip. But an analysis of US transit work trip destinations indicates that this applies in large part to just a few destinations around the nation. This is much more obvious in looking at destinations than the more typical method of analysis, which looks at the residential locations of commuters. This column is adapted from my new Heritage Foundation Backgrounder "Transit Policy in an Era of the Shrinking Federal Dollar."
Transit Legacy Cities
Transit commuting is heavily concentrated to destinations in just the six core cities (historical core municipalities) of New York, Chicago, Philadelphia, San Francisco, Boston and Washington (Backgrounder Chart 9). I call them the "transit legacy cities," because their high transit market shares relate to their development before the automobile became dominant. Because there is such a lack of clarity in the use of terms that apply to cities, it is important to emphasize that the transit legacy cities are municipalities, not the surrounding metropolitan areas or urban areas, where the majority of residents live (Note 1).
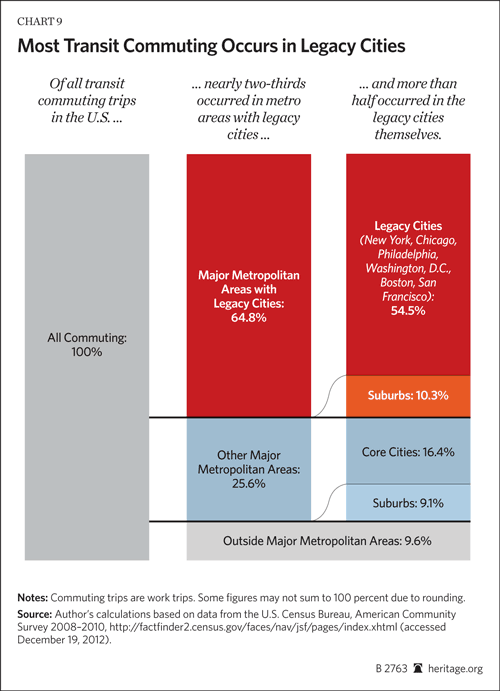
The transit legacy cities account for nearly 55 percent of the nation's transit commuters, by work trip destinations, according to the American Community Survey (2008-2010). By contrast, the transit legacy cities have an overall national employment market share barely one-tenth their national transit share (6 percent). Moreover, combined, the transit legacy cities cover a land area little larger than the core city (municipality) of Jacksonville, Florida.
At the same time, the "other side of the coin" is that commuting to other destinations is dominated by the automobile, from the suburbs in metropolitan areas with transit legacy cities, and even more so in the other 45 major metropolitan areas (with more than 1,000,000 population) and the balance of the nation.
Legacy Cities: Transit's Strength
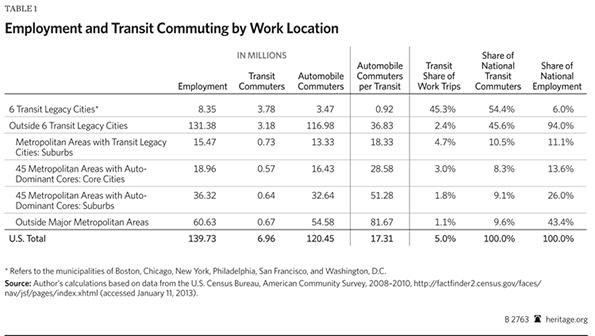
The extent of the concentration in the six transit legacy cities is illustrated in Backgrounder Table 1. In some ways, transit is, first and foremost, really a New York story. More than one-third of all transit work-trip commuting is to destinations in the core city of New York. The dominance is even greater for high-capacity subways/elevated services, a mode in which where New York represents two-thirds of national commuting.
The Key: Large, Concentrated, Well Served Downtowns: The concentration of transit commuting in the six transit legacy cities reflects the factor that is probably more responsible than any other for attracting people from cars to transit. This is a highly concentrated downtown area (central business district, or "CBD") from which a dense network of rapid transit services radiates.
The six transit legacy cities are also home to the six largest CBDs in the nation, where transit's share of commuting is far higher than compared to the rest of the nation. Approximately three quarters of commuters to the sprawling Manhattan CBD in New York (south of 59th Street) commuted by transit in 2000. Less well known is that New York also contains the CBD with the second largest transit work trip destination, downtown Brooklyn (58 percent), which is followed by downtown Chicago (55 percent).
In addition, between nearly 40 percent and more than 50 percent of commuters used transit to the CBDs of Boston, San Francisco, Philadelphia and Washington. While covering a land area less than one-half the size of Orlando's Walt Disney World, these downtowns accounted for 35 percent of national transit commuting.
Outside the Transit Legacy Cities: Automobile and Work at Home Country
So what about the 94 percent of US commuters who work outside the transit legacy cities? The answer is that the automobile dominates, and transit has been overtaken by working at home. In the suburban areas of metropolitan areas with transit legacy cities, the car carries 18 times as many people to work locations as transit. In the core municipalities of the 45 major metropolitan areas without legacy cities, cars carry 29 times as many commuters as transit, and 51 times as many in the suburbs. Outside the nation's major metropolitan areas, cars carry 82 times as many commuters as transit (Backgrounder Table 1)
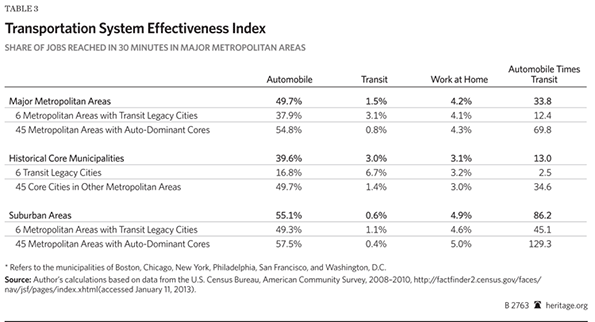
Further, outside the transit legacy cities, working at home (including telecommuting) provides access to twenty percent more jobs than transit (Backgrounder Table 3).
An American Love Affair with the Automobile?
The enduring myth of the American love affair with automobile is countered by the huge transit market shares to city downtowns . For example, commuters to Manhattan are five times as likely to use transit as cars. On the other hand, commuters to the edge city of Parsippany, on the I-287 corridor in suburban New Jersey are 50 times as likely to use their cars as transit. Yet both employment centers serve the same labor market. The issue is not preferences, it is rather rational choice. It would be irrational for most people to commute to Manhattan by car, principally because of the traffic congestion and cost, particularly for parking. It would similarly be irrational for most people to commute to Parsippany by transit, because it either could not be done at all, or it would take too long.
Transit's work trip destination market share is an effective measure of its relevance to the market.
And lest anyone should counter that the answer is more money, consider this.
A Cost Not A Revenue Problem
Portland (with a core city that is not a legacy city) has long been held out as a model for improving transit. Yet, after billions of dollars in federal and local tax subsidies, more than 50 times as many people travel to work to suburban locations by car as by transit. More than five times as many work at home as use transit, and working at home costs taxpayers virtually nothing. Yet, despite all these billions, Portland's transit system is in crisis. Tri-Met's Executive Director Neil McFarlane has warned of 70 percent service cuts over 12 years without substantial changes to union contracts.
Transit’s fundamental problem is not insufficient revenue but insufficient cost control. Since 1983, national transit expenditures have risen at an inflation-adjusted rate nine times that of its increase in commuters (Note 2). Even if costs were under control, it would be financially impossible to provide automobile-competitive transit throughout the modern urban area, as Professor Jean-Claude Ziv and I showed in our WCTRS paper (Megacities and Affluence: Transport and Land Use Considerations).
Celebrating Transit
Yet, beyond its inability to convert generous taxpayer subsidies into corresponding ridership increases, transit deserves credit for the large number of people it moves to jobs in the legacy cities. This success should be celebrated although it remains an impossible, prohibitively expensive, dream elsewhere.
Wendell Cox is a Visiting Professor, Conservatoire National des Arts et Metiers, Paris and the author of “War on the Dream: How Anti-Sprawl Policy Threatens the Quality of Life.”
----
Note 1: Each of the transit legacy cities has a lower population than the surrounding suburbs. This ranges from nearly 45 percent of the population in the suburbs of the New York metropolitan area to little more than 10 percent in Washington.
Note 2: Within the first 30 days of my time on the Los Angeles County Transportation Commission, I became convinced that transit's principal problem was cost control (see Toward More Prosperous Cities). This was then and today remains clear from the above-inflationary escalation of unit costs. Regrettably that trend continues today and has seriously impeded transit's ability to increase ridership.
-----
Photo: Downtown Philadelphia (by author)